Scientists create a genomic reference database for the Russian population
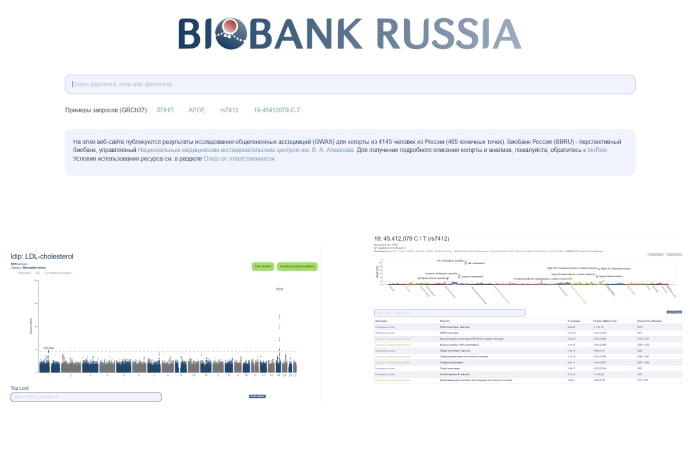
Scientists at the Research Department of Genetic Risks and Personalized Prevention of the WCRC for Personalized Medicine have created the first in Russia genomic reference database for the Russian population as an open-source platform for the results of genome-wide association studies.
The search for associations between inherited DNA variants and disease risks is one of the main tasks of predictive medicine in order to timely identify and prevent unhealthy phenotypes. Large projects such as UK Biobank, FinnGen and Biobank Japan have greatly contributed to the search for these associations, the development of personalized medicine and the discovery of new drug targets. However, the growing ethnic diversity of genetic studies has led to the discovery of population-specific loci that can only be identified in a specific population. Of particular interest is the multinational Russian population, which has a unique genetic structure characterized by various combinations of European and Asian haplotypes. Therefore, studies of polygenic traits in the Russian population can become not only a powerful source for the replication of population-specific associations found in the largest biobanks, but also a resource for new genetic associations specific to Finno-Ugric and Siberian peoples. Moreover, the ultimate goal of such studies is the ability to effectively predict individual innate risks of diseases, which largely depends on the genetic characteristics of the population. As shown earlier, polygenic risk models are poorly transferred between populations, which is an important argument for building a large-scale database of genome-wide association studies in Russia.
Scientists at the WCRC for Personalized Medicine have shown that the genetic structure of the Russian population in urban areas of the European and central parts consists of a number of subpopulations with a high degree of kinship to Finnish and East Asian peoples. Genome-wide association study (GWAS) was performed to analyze 465 traits, including blood biomarkers and polygenic diseases.
The results were used to create the first in Russia resource with data from studies of polygenic traits as the largest open-source reference on allele frequencies and genetic associations, which can become the core for further study of the genetics of polygenic traits in the Russian population. One main problem that remains to be solved is the scaling of GWAS in the Russian Federation to other large biobanks.
The results of the study are available here.
