Results of the study of a rare genetic neuromuscular disorder
The scientists of the World-Сlass Research Centre for Personalized Medicine (WCRC) published an article summarizing the results of a study that was conducted in the area of unknown, rare and genetically determined diseases and focused on Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD), a rare genetic neuromuscular disorder, with regard to cardiovascular disease.
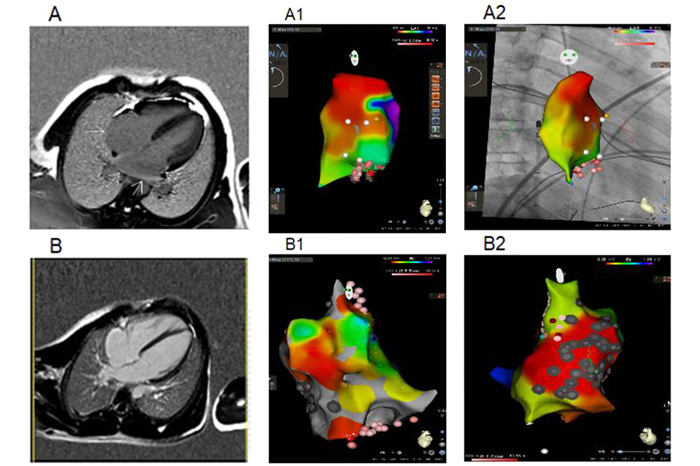
This disease in most cases debuts with a muscular phenotype, and heart damage manifests itself later and is uncommon in children, however, they may have a severe course associated with life-threatening conditions. Its incidence in the pediatric population is about 0.22 per 100,000. The article described 5 atypical clinical cases with various forms of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy caused by mutations in the EMD and LMNA genes, with early onset of cardiovascular symptoms manifested as complex heart rhythm and conduction disorders and the absence of a marked muscle phenotype.
The study combined the results of standard screening with high-tech diagnostic methods to determine a personalized therapeutic strategy using modern treatments, including radiofrequency ablation and implantation of antiarrhythmic devices, and show the importance of thorough targeted neurological and genetic screening for neuromuscular disorders in children with complex progressive heart rhythm and conduction disorders, even in the absence of typical muscular manifestations.
This study is fully in line with the topic of the WCRC on identifying unknown rare and genetically determined diseases and it was possible only due to the availability of high-tech equipment and the ability to conduct a world-class testing and treatment involving specialists from several divisions of Almazov Centre and research departments of the WCRC: specialists from the laboratory for the registry of rare understudied diseases, pediatric cardiologists and neurologists, arrhythmologists, radiologists, laboratory diagnosticians, pathologists.
A large amount of testing was carried out in the molecular genetic laboratory using new generation sequencing, and a large amount of literature and information was analyzed.
Publication link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8137911/
07.05.2021
